As we could learn from previous readings:
Virtualization helps us to create virtual versions of a computer resource such as devices, storage, networks, servers, or even applications.
It allows organizations to partition a single physical computer or server into several virtual machines (VM).
Each VM can then interact independently and run different operating systems or applications while sharing the resources of a single computer.
Some advantages of Virtualization are:
- Enhanced performance
- Promotes the use of resources in an optimum manner
- Space saving
 and Containerization:
and Containerization:
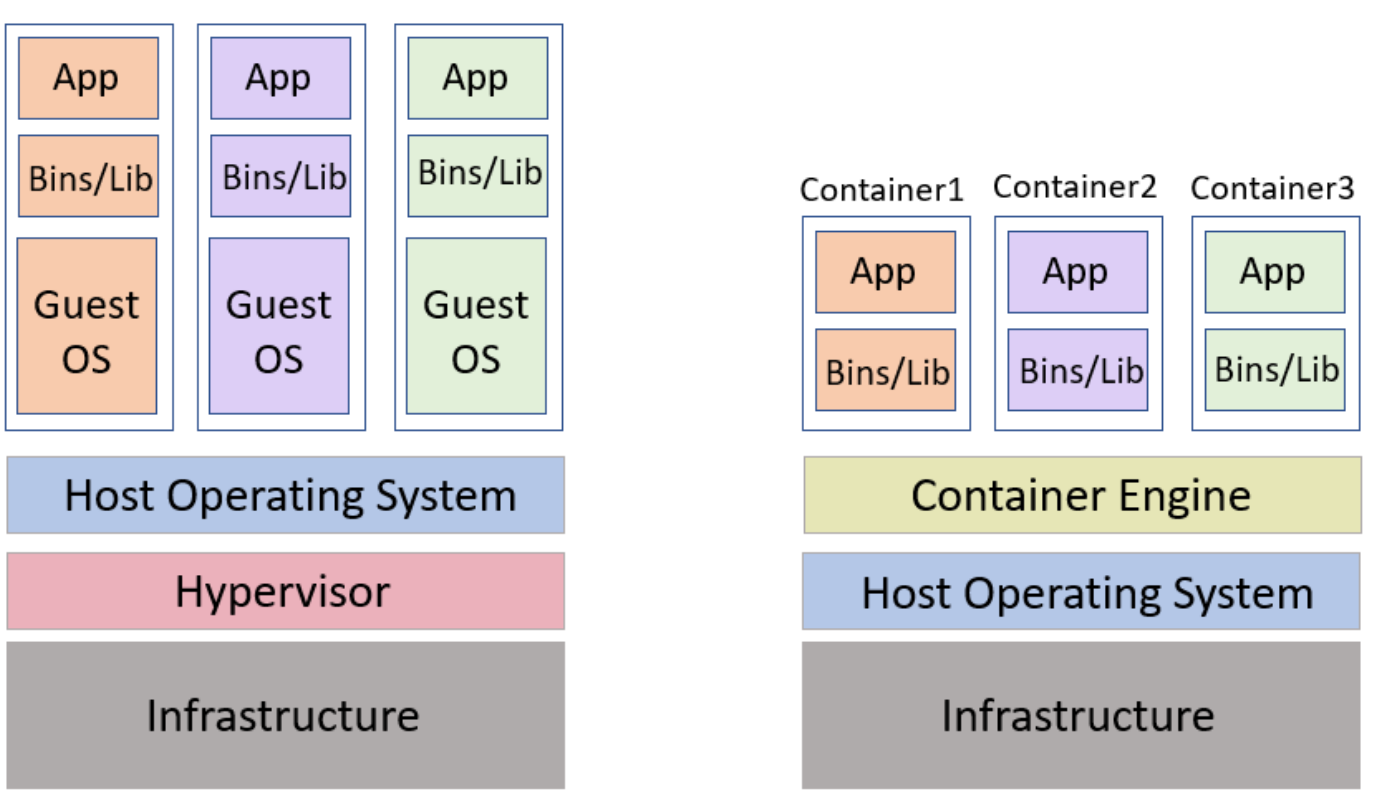
Containerization is a lightweight alternative to virtualization. This involves encapsulating an application in a container with its own operating environment.
Thus, instead of installing an OS for each virtual machine, containers use the host OS. Since they don’t use a hypervisor, you can enjoy faster resource provisioning.
Some advantages of Containerization are:
- Containers share the machine’s operating system Kernel. They do not require to associate the operating system from within the application hence they are lightweight.
- It takes less start-up time in the environment where it is deployed.
- It’s ideal for automation and DevOps pipelines, including continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) implementation.
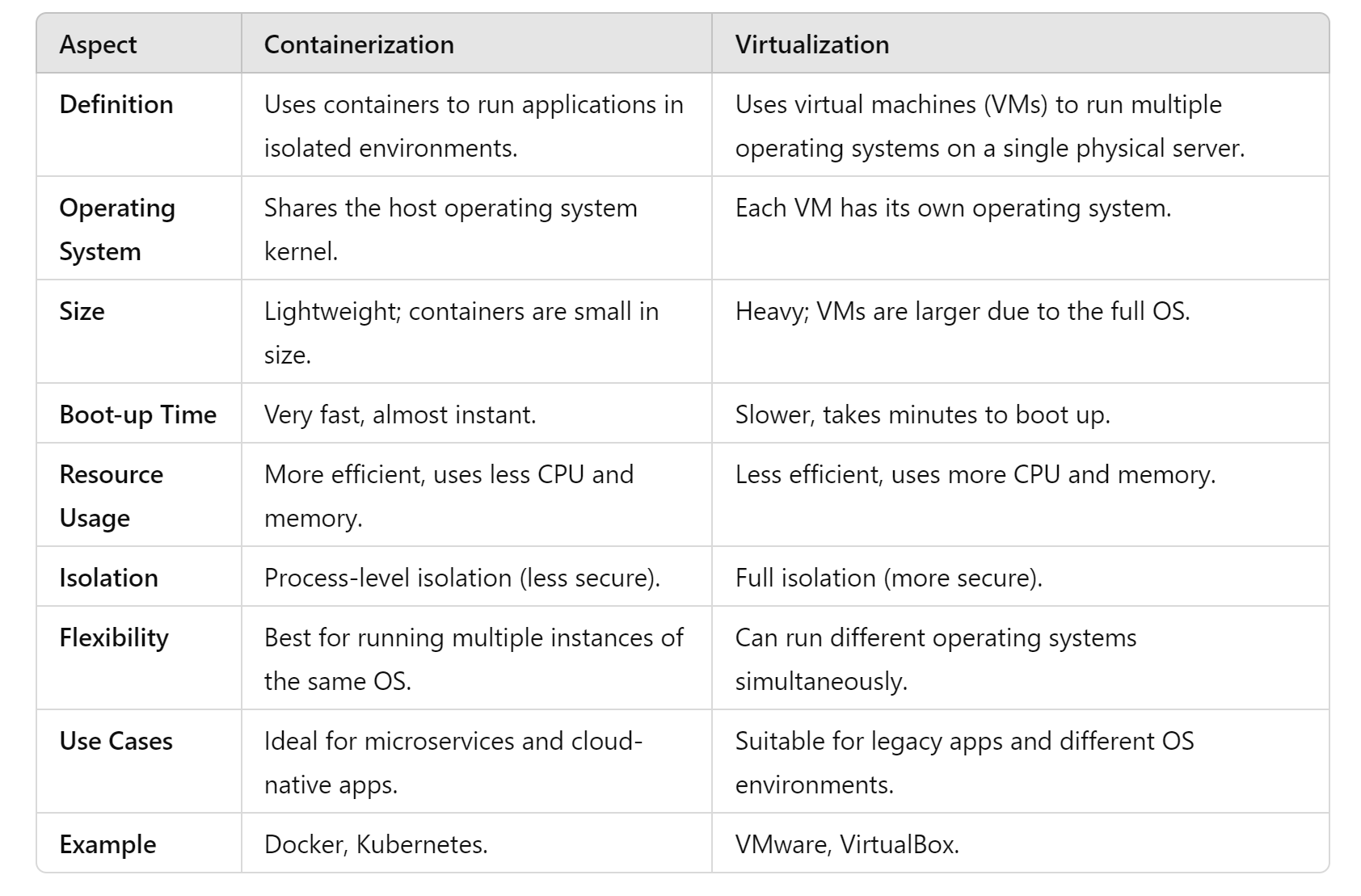
Some of the differences between containerization and virtualization are: